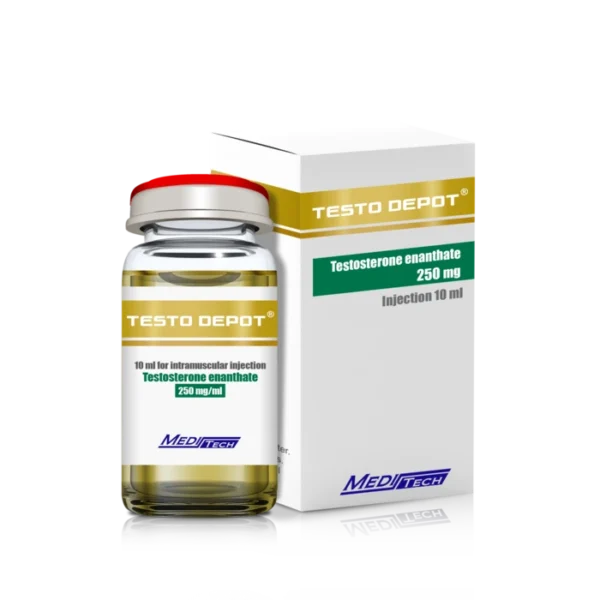

Testosterone Meditech
0 out of 5
$63.00
250 mg/ml x 10ml vial
- Description
- Additional information
- Reviews (0)
Description
Injectable Testosterone Meditech for sale
Testosterone, the driving force behind male vitality, shapes everything from muscle strength to mental clarity. Meditech’s Testosterone, a pharmaceutical-grade injectable, is designed for those looking to address low hormone levels or push their physical performance to new heights. Whether you’re considering testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) or exploring its role in bodybuilding, this guide covers the essentials—benefits, safe use, costs, and legal considerations—to help you make informed decisions.
What is Testosterone Replacement Therapy?
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) is a medical treatment for men with low testosterone, often due to hypogonadism or age-related decline. Symptoms like fatigue, low libido, and muscle loss can signal the need for TRT. Meditech’s Testosterone, typically administered via injection, restores levels to a normal range (300-1000 ng/dL for men). The process starts with a doctor’s evaluation, including blood tests to confirm low levels. If approved, TRT can improve energy, mood, and overall quality of life. Online clinics simplify access, but a prescription is required for legal use.
How to Get Prescribed Testosterone?
Getting a testosterone prescription involves a clear path. First, schedule a consultation with a healthcare provider—either in-person or via telemedicine. You’ll discuss symptoms like low energy, erectile dysfunction, or reduced muscle mass. A blood test measures your testosterone levels; results below 300 ng/dL often qualify for TRT. Meditech’s injectable testosterone is a common choice, prescribed in 10ml vials (250mg/ml). Reputable online platforms, like those following DEA guidelines, can provide prescriptions after lab verification, ensuring safety and legality. Always avoid sources skipping these steps—they’re often selling risky, unregulated products.
Testosterone Bodybuilding Benefits
In bodybuilding, Meditech’s Testosterone is a powerhouse. It boosts protein synthesis, leading to faster muscle growth and repair. Users report strength gains, better endurance, and quicker recovery between sessions. Typical cycles last 8-12 weeks, with doses of 200-600mg weekly, often stacked with steroids like Dianabol for bulking or Winstrol for cutting. These stacks amplify results but increase side effect risks. Post-cycle therapy (PCT) with drugs like Clomid is essential to restore natural hormone production, preventing crashes. Meditech’s formulation is praised for its smooth injections, minimizing discomfort.
Testosterone Side Effects
Testosterone use carries risks. Common side effects include acne, fluid retention, and increased hair growth. Higher doses can cause more serious issues, like elevated red blood cell counts (raising clot risks), gynecomastia, or mood swings. Long-term use may suppress natural testosterone production, impacting fertility. In rare cases, heart strain or prostate issues emerge, especially without monitoring. Women using testosterone off-label risk voice deepening or excessive hair growth. Regular blood tests and doctor oversight help manage these risks, ensuring safer use.
How Much Does Testosterone Therapy Cost?
Costs for Meditech’s Testosterone vary. A 10ml vial (250mg/ml) typically ranges from $50-$90, depending on the supplier and region. TRT patients may need 1-2 vials monthly, while bodybuilders using higher doses may spend more. Insurance often covers TRT for medical use, lowering out-of-pocket costs, but bodybuilding use is usually self-funded. Online pharmacies and telemedicine services can reduce expenses, but prioritize vendors with verified products. Hidden costs, like blood tests or PCT drugs, should also be factored in.
Where to Get Testosterone?
Meditech’s Testosterone is available through licensed pharmacies or trusted online suppliers, but only with a prescription in regulated countries like the USA, where it’s a Schedule III substance. Check for authenticity—Meditech’s products should have verifiable codes on packaging. Avoid unregulated sellers, as counterfeit steroids are common and dangerous. Prices are competitive, but quality trumps savings. Telemedicine platforms can connect you with legitimate sources, streamlining the process while ensuring compliance.
Meditech’s Testosterone is a potent tool for TRT or bodybuilding, offering benefits like renewed energy and muscle gains. Its power comes with responsibility—legal sourcing, medical guidance, and health monitoring are non-negotiable. Whether you’re addressing low testosterone or chasing fitness goals, start with a doctor’s advice to ensure it’s the right path for you.
Additional information
| Bottle type | Ampoules, Vial |
|---|
Be the first to review “Testosterone Meditech” Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a review.
Related Products
Bulking steroids for sale, Buy Dianabol Online, Oral steroids for sale
Dianabol Meditech
0 out of 5
$35.00
Bulking steroids for sale, Buy Trenbolone, Injectable steroids for sale
Tren Enanthate Meditech
0 out of 5
$115.00



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.